What is pneumonia?
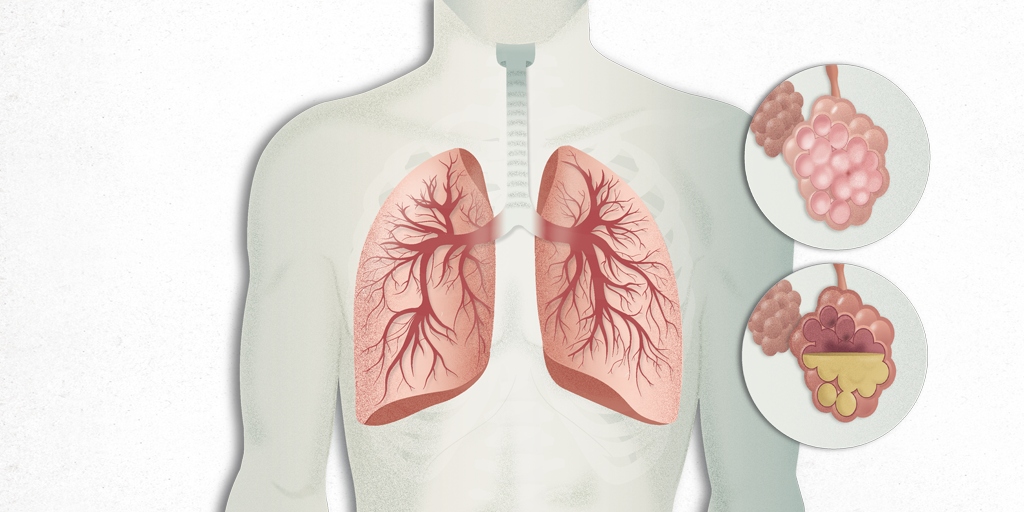
It is a respiratory illness caused by inflammation of the lung, causing solidification of the lung., commonly due to infection which leads to the loss of the normal sponginess of the lungs.
Types of pneumonia : –
- Community acquired pneumonia
- Hospital acquired pneumonia
- Pneumonia in immunocompromised host.
Causes of Pneumonia
- Infection by various organisms like bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa
- Chemical agents – irritant gases, aspiration of vomit (vomit entering the lungs accidentally)
- Physical agents – radiation
- Hypersensitivity reactions – Lupus etc
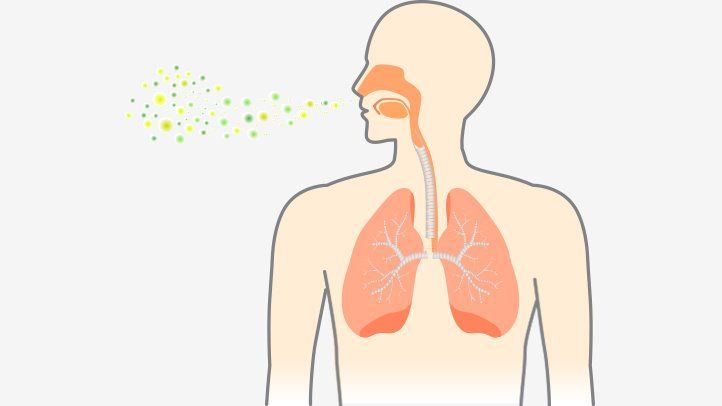
How does pneumonia spread?
It spreads through droplets which is inhaled. Lack of hygiene, overcrowding and poor sanitation is a huge factor that causes an increase in the spread of pneumonia.
Predisposing Factors for Pneumonia/ Risk Factors
- Extreme age groups – very old people and children.
- Indoor air pollution
- Pre existing upper respiratory tract infections.
- Other co existing conditions like diabetes and heart failure
- Smoking
- Alcohol
- HIV
- Person taking steroid medication and other immunosuppressant drugs
- Other respiratory conditions like cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis and COPD.

Symptoms of Pneumonia
Onset of symptoms varies depending on which organism is causing it, but is usually within a week to 10 days.
COUGH – cough is short, painful and dry initially but later cough is associated with sputum, which varies in colour, depending on the infective organism, most commonly it is due to a bacteria called streptococcus and the sputum is rusty in colour but it can be green in cases of pseudomonas infection or black or yellow, depending on the causative organism.
Cough can be associated with blood, sputum will be blood tinged and will look bright red.
CHEST PAIN – sudden, intense, sharp, stabbing or burning pain while breathing. This occurs due to inflammation of a structure called the pleura which covers the lung and acts as a protective mechanism for the lungs
Pain can spread to shoulder and upper abdomen as well.
BREATHLESSNESS – The inflammation in the lungs causes accumulation of fluid in the alveoli of the lungs causing difficulty in breathing

OTHER GENERAL FEATURES
- Decreased appetite
- Discomfort
- Myalgia, which is general pain in skeletal muscles causing difficulty to move.
- Headache
- Tiredness
FEVER – Fever is characteristic of almost all acute infections, it is either moderate in cases of bacterial infections or very high in cases of viral infections.
LOW OXYGEN SATURATION – causing bluish discolouration of tongue, this happens because the diseased lungs are not able to adequately allow exchange of gases and the arteries carry lesser oxygen to the rest of the organs and tissues of the body.
ON EXAMINATION OF THE PATIENT
- Increased respiratory rate
- Increased pulse rate
- BP may be low
WHEN TO GET HOSPITALISED
- Elderly patients over the age of 65
- Severe breathlessness and increased respiratory efforts
- Bluish discolouration of tongue and mucosa of the mouth (known as central cyanosis)
- Fall in BP
- Spread of infection
- Altered mental state
- Shock – very high fever, seizures, feeble pulse, altered mental status
- Very low oxygen saturation
Atypical Pneumonia– In some rare cases of pneumonia, cough, breathlessness and chest pain is lesser but other manifestations such as fatigue, fever is more. Usually observed in pneumonia caused due to viruses, legionella, mycoplasma and chlamydia.
Pneumonia in Children
This deserves special attention as pneumonia in children is a leading cause of mortality in children in India, especially under 5 years of age.
Risk factors –
- Low birth weight
- Premature baby
- Failure of breastfeeding
- Undernutrition
- Lack of vaccination
- Very young infant (up to 2 months of age)
- Vitamin A deficiency (Vitamin A helps in maintaining the structure and integrity of the lining of the respiratory tract and protects it from infections)
Prevention Of Pneumonia in Children
GENERAL PROTECTIVE MEASURES
- Regular check ups during pregnancy to ensure a healthy baby and prevent prematurity of the baby and prevent transmission of infection to the baby in case the mother has it.
- Babies with low birth weight need special attention and care.
- Adequate nutrition of children
- Ensure good hygiene at home, wash hands before preparing food, teach children to wash hands frequently.
- Limiting size of family to prevent overcrowding and further spread of disease in the community.
- EXCLUSIVE BREASTFEEDING till 6 months of age
- Educate mother to recognise danger signs in the baby (fast breathing, crying, fever, failure of child to grow, refusal of food and chest appears inwards)
SPECIFIC PROTECTIVE MEASURES
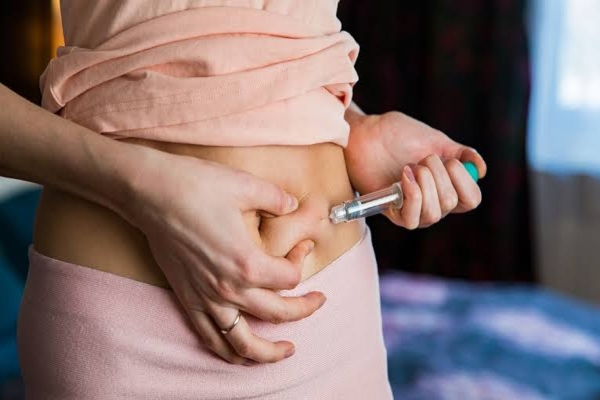
Proper, regular vaccination – pneumococcal vaccination at 6 weeks and 14 weeks, followed by a booster at 9 months of age is now introduced in the National Immunisation Schedule.
Oral Vitamin A for children between 9 months and 5 years, this also prevents vitamin A deficiency and protective for the eyes and other infections.
Prevention of Spread of Pneumonia in Adults
- Try to avoid risk factors such as smoking and drinking.
- Good, well balanced diet that promotes immunity, preferably containing lots of fruits and vegetables which are rich in vitamins.
- Exercise, yoga and meditation to regulate breathing.
- WASH HANDS REGULARLY
- Stay away from sick people, especially those who are coughing.
- Take extra precaution if you have predisposing conditions or immunosuppressed.
- PNEUMOCOCCAL VACCINE is advised for patients more than 65 years of age and also those with COPD, diabetes, asthma.
- Influenza vaccine is also recommended every year to those with high risk of mortality.
Complications Of Pneumonia
- Respiratory failure
- Spread of infection causing
- Meningitis
- Abscess
- Sepsis (emergency condition)
- Heart valve infections
- Heart wall infections
Mild cases of pneumonia can be managed at home
- Lots of fluid intake
- Adequate bed rest
- Ginger tea, lime juice
- Do not go outside till symptoms resolve
- Do not cough on others
- If antibiotics are prescribed, take them as advised, without skipping.
RECURRENT PNEUMONIA, i.e if individual gets pneumonia frequently, it indicates underlying condition and requires thorough examination and proper diagnosis and must not be dismissed.
Pneumonia is difficult to eradicate but with the availability of antibiotics, increased awareness and promotion of healthy lifestyle, the mortality and morbidity of pneumonia can be significantly reduced and hospital admission can also be prevented if patient is aware of warning signs and methods of prevention.